Optical characterization of solar reflectors
Short description
CEA (a French governmental organization) is involved in ageing and characterization of CSP components since many years.
Solar reflector characterization by optical inspection (microscopy) and optical measurement of reflectance (spectral hemispherical reflectance, monochromatic specular reflectance, spectral specular reflectance and colorimetric)
Main technical features
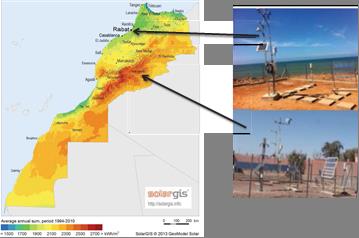
Polymeric mirrors have been exposed for a period of approximately 250 days at both coastal and desertic sites. At the end of the 250 days, all polymeric mirrors show an apparition of abrasion impacts on their surfaces due to sand particles or to the cleaning scratches.
Optical microscope images show the degradation effects taking place on the polymer mirrors on both coastal site and desertic outdoor sites. Mirror degradation is characterized by specular reflectance measurements using an UV-NIR-Vis Perkin Elmer Lambda 950 equipped with ARTA (Absolute Reflectance and Transmittance Analyzer) accessory. It allows measurements at different incidence angles and at each wavelength on the whole solar spectrum from 280 nm to 2500 nm.
Reflectors consist of solar mirrors which can be produced out of various materials (glass, aluminium or polymer). Those mirrors must guarantee a high reflectance and a strong resistance to both physico-chemical and mechanical degradations that may be caused by the environment to which they are exposed.
Every month, samples are controlled on exposure sites by measuring their specular reflectance before and after cleaning. Reflectance is measured for all samples using a portable spectrophotometer (Devices and Services 15R manufactured and services) which allows measuring the specular reflectance at 660nm with 15° incidence angle and 12.5mrad acceptance angle in the center of the sample at three to five different points.
For the measurements of reflectance, specular reflectance decreases. This variation is induced by different defects observed at mirrors surfaces.
The loss of specular reflectance have also been conducted on the corroded areas.
Specular reflectance measured after cleaning laminated samples exposed at both sites
Innovative aspects
After about one year of natural ageing of polymeric and glass mirrors, a conclusion on polymeric mirrors can be drawn:
- Polymeric mirrors show various types of degradation at both coastal and desertic sites causing a significant decrease of specular reflectance.
Applications
The first round robin test was performed in 2010 with only three organizations participating.
In order to speed up the discussion around the guidelines, a second round robin test was launched at the beginning of 2013. That one is named SolarPACES Reflectance Round Robin (SRRR), has two goals: i) verify the reliability of the procedure for evaluating the solar-weighted hemispherical reflectance as suggested by the guidelines, and ii) stimulate each research institute to develop instrumentation and methods for evaluating off-normal near-specular solar reflectance.
Each research institute used a high quality spectrophotometer, equipped with an integrating sphere with diameter not less than 150 mm.
Related documents
Image gallery
Type of partner sought
...Tasks to be performed by the partner you are looking for.
Polymeric and glass mirrors were exposed in two Moroccan sites with characteristic weather conditions, one close to the ocean and one in the desert.
MASCIR (Moroccan foundation for advanced Science, Innovation and Research-Morocco) and CEA (French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission) collaborate in a study with the main objective to understand the mechanisms of degradation occurring at each kind of mirror tested.